Can Seborrheic Dermatitis Lead to Hair Loss?
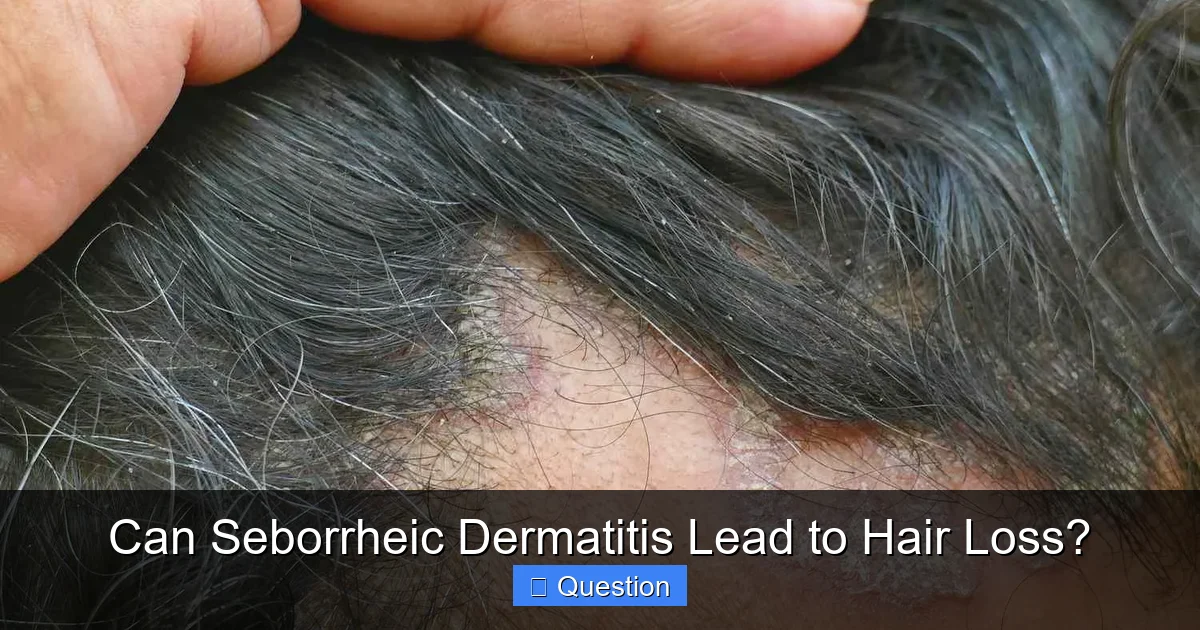
Seborrheic dermatitis can indeed contribute to temporary hair loss, primarily due to chronic inflammation, excessive scratching, and disruption of the hair growth cycle. While the hair loss is typically not permanent, early and consistent management of the underlying condition is crucial to prevent further thinning and promote healthy regrowth. Addressing the inflammation and maintaining a healthy scalp environment are key steps to mitigate this concern.
You’ve probably heard of seborrheic dermatitis, perhaps by its more common name: dandruff. It’s that pesky, often embarrassing, scalp condition that brings flakiness, itchiness, and sometimes even redness. For many, it’s a minor inconvenience, easily managed with an over-the-counter shampoo. But for others, the symptoms can be more severe, impacting their daily lives and raising a concerning question: can seborrheic dermatitis lead to hair loss?
It’s a valid concern, and one that often causes a lot of anxiety. While seborrheic dermatitis is incredibly common, affecting millions worldwide, the thought of it potentially leading to hair thinning or baldness can be distressing. After all, our hair plays a big role in how we feel about ourselves, right? So, let’s dive deep into this topic, separating fact from fear, and understanding exactly what’s going on with your scalp and hair when seborrheic dermatitis is present.
We’ll explore the underlying mechanisms, discuss how seborrheic dermatitis might impact your hair follicles, and most importantly, arm you with practical, actionable strategies to manage the condition and protect your precious strands. If you’ve been losing sleep over your flaky, itchy scalp and wondering if hair loss is inevitable, you’ve come to the right place. Let’s get some clarity!
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the Link: Seborrheic dermatitis can cause temporary hair loss through inflammation, itching, and disruption of the hair growth cycle, but it’s rarely permanent.
- Inflammation is Key: Chronic inflammation of the scalp, a hallmark of seborrheic dermatitis, directly damages hair follicles and can hinder healthy hair growth.
- Scratching Aggravates: Persistent scratching due to the intense itchiness associated with seborrheic dermatitis can physically dislodge hairs and further irritate follicles.
- Reversible Condition: Hair loss caused by seborrheic dermatitis is typically reversible once the underlying scalp condition is effectively managed and inflammation subsides.
- Effective Treatment is Crucial: Consistent use of medicated shampoos, topical treatments, and adopting gentle hair care practices are vital for controlling symptoms and promoting hair regrowth.
- Lifestyle Matters: Stress management, a balanced diet, and avoiding harsh hair products can significantly improve scalp health and reduce flare-ups of seborrheic dermatitis.
- Seek Professional Advice: If you suspect seborrheic dermatitis or are experiencing significant hair loss, consulting a dermatologist is recommended for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
📑 Table of Contents
- What Exactly is Seborrheic Dermatitis?
- The Direct Link: Can Seborrheic Dermatitis Lead to Hair Loss?
- Recognizing Hair Loss Associated with Seborrheic Dermatitis
- Effective Strategies to Manage Seborrheic Dermatitis and Prevent Hair Loss
- Long-Term Outlook: Reversing Hair Loss and Maintaining Scalp Health
- Conclusion
What Exactly is Seborrheic Dermatitis?
Before we tackle the hair loss question, let’s make sure we’re all on the same page about what seborrheic dermatitis actually is. Think of it as a common, chronic inflammatory skin condition. It primarily affects areas of the body that have a lot of oil (sebaceous) glands. This includes your scalp, face (especially around the nose, eyebrows, and ears), chest, and even the armpits or groin. When it shows up on your scalp, we often call it dandruff, but it can be much more than just a few flakes.
Typical symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis include red, greasy skin covered with flaky white or yellowish scales. It can be incredibly itchy, sometimes even burning. For babies, it’s known as “cradle cap.” While it’s not contagious and doesn’t indicate poor hygiene, it can definitely make you feel self-conscious.
Understanding the Causes and Triggers
The exact cause of seborrheic dermatitis isn’t fully understood, but it’s believed to be a combination of factors. One of the main culprits is a type of yeast called Malassezia. This yeast naturally lives on everyone’s skin, but in people with seborrheic dermatitis, it somehow triggers an inflammatory response. It’s not an infection in the traditional sense, but rather an overreaction by the body to this common skin inhabitant.
Other factors can trigger or worsen flare-ups. These include:
- Genetics: It tends to run in families.
- Stress: Emotional or physical stress can definitely make symptoms worse.
- Hormonal changes: Fluctuations in hormones can play a role.
- Weakened immune system: People with certain medical conditions, like HIV or Parkinson’s disease, are more prone to severe seborrheic dermatitis.
- Cold, dry weather: Many people find their symptoms worsen in winter.
- Certain medications: Some drugs can trigger or exacerbate the condition.
Understanding these triggers can be the first step in managing your seborrheic dermatitis effectively.
Common Symptoms Beyond Flakes
While flaking is the most well-known symptom, seborrheic dermatitis can manifest in other ways, especially on the scalp. You might notice:
- Redness: Inflamed patches on the scalp.
- Greasy or oily patches: Despite the flaking, affected areas can feel greasy.
- Intense itching: This is often the most bothersome symptom and can lead to scratching.
- Crusting: In more severe cases, thick, yellow or brown crusts might form.
- Burning sensation: The inflamed skin can feel sore or burn.
It’s this chronic inflammation and irritation that brings us closer to answering our main question: can seborrheic dermatitis lead to hair loss?
The Direct Link: Can Seborrheic Dermatitis Lead to Hair Loss?
Now for the big question: can seborrheic dermatitis lead to hair loss? The short answer is yes, it absolutely can, but it’s important to understand the nuances. The good news is that hair loss caused by seborrheic dermatitis is typically temporary and reversible once the underlying condition is brought under control. It’s rarely a cause of permanent baldness.
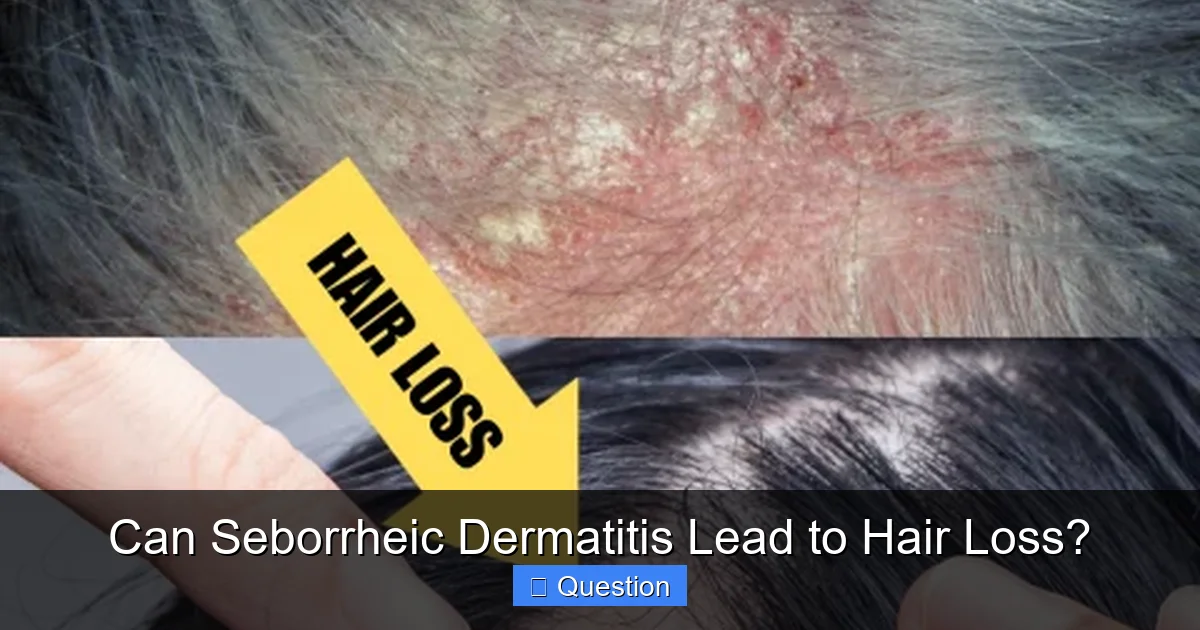
Visual guide about Can Seborrheic Dermatitis Lead to Hair Loss?
Image source: hairtransplantnetwork.com
The primary mechanisms through which seborrheic dermatitis can contribute to hair loss involve inflammation, physical trauma from scratching, and a disruption of the normal hair growth cycle. Let’s break down how each of these plays a role.
How Inflammation Harms Hair Follicles
Chronic inflammation is the main culprit here. Seborrheic dermatitis creates an inflammatory environment on your scalp. This constant inflammation around the hair follicles can directly damage them. Think of it like a garden where the soil is always irritated and inflamed – it’s hard for plants to grow strong and healthy, right? The same goes for your hair.
When follicles are consistently inflamed, they may:
- Produce weaker hair: Hairs that do grow might be thinner, more brittle, and prone to breaking.
- Enter a resting phase prematurely: The inflammatory signals can prematurely push hair follicles from the active growth phase (anagen) into the resting phase (telogen), leading to increased shedding.
- Be unable to anchor hair properly: The foundation for hair growth becomes compromised, making hairs fall out more easily.
Over time, if the inflammation from seborrheic dermatitis is left unchecked, it can lead to noticeable hair thinning and shedding. This is why addressing the inflammation is crucial if you’re concerned about hair loss.
The Role of Scratching and Trauma
Let’s be honest, the itchiness from seborrheic dermatitis can be maddening. It’s incredibly tempting, almost impossible, not to scratch. But this constant scratching, while providing temporary relief, can physically harm your hair and scalp. Vigorous scratching can:
- Physically dislodge hairs: You’re literally pulling hairs out of their follicles before they’re ready to shed naturally.
- Damage the hair shaft: Repeated scratching can weaken the hair strand itself, making it more prone to breakage.
- Further irritate the scalp: Scratching can break the skin, introducing bacteria and potentially leading to secondary infections, which only worsen the inflammatory cycle.
So, while the initial cause is the seborrheic dermatitis itself, your reaction to the itch can definitely accelerate hair loss.
Impact on the Hair Growth Cycle
Your hair goes through a continuous cycle of growth (anagen), regression (catagen), and rest (telogen), followed by shedding and new growth. A healthy scalp ensures this cycle proceeds smoothly. However, seborrheic dermatitis can throw a wrench into this process.
The constant inflammation and stress on the follicles can shorten the anagen (growth) phase and prolong the telogen (resting) phase. This means more hairs enter the resting phase and shed earlier than they normally would. The result? More hair fall and a noticeable decrease in overall hair density. If the scalp environment remains hostile, the new hairs that try to grow might also struggle, contributing to the perceived hair loss.
It’s a cycle: seborrheic dermatitis leads to inflammation and itching, which can lead to scratching and hair loss, which then further stresses the follicles. Breaking this cycle is key to promoting healthy hair regrowth.
Recognizing Hair Loss Associated with Seborrheic Dermatitis
If you have seborrheic dermatitis and are noticing more hair in your brush or shower drain, it’s natural to worry. But how do you know if that hair loss is truly related to your scalp condition and not something else? Recognizing the pattern can help you understand the problem better.
What Does This Hair Loss Look Like?
Hair loss from seborrheic dermatitis typically manifests as:
- Increased shedding: You’ll likely see more hair falling out than usual, particularly when shampooing or brushing.
- Diffuse thinning: Unlike some other types of hair loss that create distinct bald patches, hair loss due to seborrheic dermatitis often results in a general thinning across the affected areas of the scalp.
- Located on inflamed areas: The hair loss will generally be most prominent in the areas where your seborrheic dermatitis is most active – typically the crown, temples, and along the hairline.
- Accompanied by other symptoms: Crucially, this hair loss will almost always be accompanied by the tell-tale signs of seborrheic dermatitis: redness, flaking, itchiness, and possibly greasy patches.
You might also notice that the shed hairs have tiny white or yellowish flakes attached to their roots, indicating they originated from an inflamed scalp environment.
Differentiating from Other Hair Loss Types
It’s important to distinguish hair loss from seborrheic dermatitis from other common types of hair loss. For example:
- Androgenetic Alopecia (Pattern Baldness): This is genetic and results in a distinct pattern – receding hairline and thinning at the crown for men, and diffuse thinning over the top of the scalp for women. It typically doesn’t involve significant scalp inflammation or itch.
- Telogen Effluvium: This is a temporary shedding of hair due to a stressful event (illness, surgery, childbirth, severe stress). It causes widespread thinning but usually resolves on its own once the stressor is removed, and often without the prominent scalp symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis.
- Alopecia Areata: This causes patchy, circular bald spots and is an autoimmune condition. The scalp in affected areas is usually smooth and not inflamed or flaky.
If your hair loss is accompanied by a persistently itchy, red, and flaky scalp, it’s highly probable that seborrheic dermatitis is playing a significant role.
Effective Strategies to Manage Seborrheic Dermatitis and Prevent Hair Loss
The good news is that by effectively managing your seborrheic dermatitis, you can often reverse the associated hair loss and promote healthy regrowth. The key is consistency and finding a treatment plan that works for you. Here are some strategies:
Medicated Shampoos: Your First Line of Defense
Medicated shampoos are often the cornerstone of seborrheic dermatitis treatment. They contain active ingredients designed to combat the yeast and reduce inflammation. Look for ingredients like:
- Zinc pyrithione: An antifungal and antibacterial agent.
- Selenium sulfide: Another antifungal, also helps reduce cell turnover.
- Ketoconazole: A powerful antifungal that specifically targets Malassezia yeast.
- Salicylic acid: Helps soften and remove scales.
- Coal tar: Reduces inflammation and slows skin cell growth.
Tip: For best results, leave the shampoo on your scalp for 5-10 minutes before rinsing, allowing the active ingredients to work. You might need to use it a few times a week, then taper down as symptoms improve. Rotate between different active ingredients if one stops being as effective.
Topical Treatments and Scalp Care
Beyond shampoos, your dermatologist might recommend topical solutions, especially for stubborn patches or more severe inflammation caused by seborrheic dermatitis:
- Topical corticosteroids: Mild steroid creams or lotions can quickly reduce inflammation and itching. These are usually used for short periods to avoid side effects.
- Calcineurin inhibitors (e.g., pimecrolimus, tacrolimus): These non-steroid creams can help reduce inflammation and are often used for longer-term management.
- Antifungal creams: Sometimes, specific antifungal creams are prescribed to directly target the Malassezia yeast.
Practical Example: If you have a particularly stubborn red patch behind your ears or along your hairline, your doctor might prescribe a low-potency steroid lotion to apply directly to that area, complementing your medicated shampoo routine.
Lifestyle Adjustments for a Healthier Scalp
Your lifestyle plays a significant role in managing seborrheic dermatitis. Simple changes can make a big difference:
- Stress Management: Stress is a known trigger for flare-ups. Incorporate stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or spending time in nature.
- Balanced Diet: While not a cure, a healthy diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins (especially B vitamins and zinc), and antioxidants can support overall skin health and potentially reduce inflammation.
- Limit Alcohol and Sugary Foods: Some people find that reducing alcohol and high-sugar foods helps manage their symptoms, as these can sometimes contribute to inflammation or yeast overgrowth.
- Sunlight Exposure: A little natural sunlight can sometimes help. However, always protect your skin from excessive UV exposure.
These adjustments can help create a less hospitable environment for seborrheic dermatitis on your scalp.
Gentle Hair Care Practices
How you treat your hair and scalp matters, especially when dealing with seborrheic dermatitis:
- Avoid Harsh Products: Steer clear of hair sprays, gels, mousses, and other styling products that can build up on your scalp or irritate it. Choose mild, hypoallergenic products where possible.
- Wash Regularly: Don’t be afraid to wash your hair regularly. Frequent washing with medicated shampoos can help control oil and flake buildup. Just be gentle.
- Be Gentle When Brushing/Combing: Avoid aggressive brushing, especially when your hair is wet and more vulnerable. Use a wide-tooth comb and be extra careful to prevent physically dislodging hairs.
- Avoid Scratching: This is easier said than done, but try your best! If the itch is unbearable, try gently patting the area or using a cool compress. Keep your nails short to minimize damage if you do scratch.
When Professional Help is Needed
If over-the-counter treatments aren’t working, your symptoms are severe, or you’re experiencing significant hair loss, it’s crucial to see a dermatologist. They can:
- Provide an accurate diagnosis and rule out other conditions.
- Prescribe stronger medicated shampoos or topical treatments.
- Offer advanced therapies if necessary.
- Help you understand the specific nature of your hair loss and recommend solutions.
Don’t hesitate to seek professional guidance, especially if your seborrheic dermatitis is leading to hair loss and affecting your quality of life.
Long-Term Outlook: Reversing Hair Loss and Maintaining Scalp Health
It’s important to approach the management of seborrheic dermatitis with a long-term perspective. This condition is often chronic, meaning it can flare up periodically. However, with consistent care, you can keep symptoms under control and minimize the impact on your hair.
Is the Hair Loss Permanent?
One of the most reassuring facts to remember is that hair loss from seborrheic dermatitis is almost always temporary. Once the inflammation on your scalp is reduced and the condition is managed, your hair follicles can recover, and healthy hair growth can resume. It might take some time – hair growth is a slow process – but with patience and persistent treatment, you should see improvement.
Permanent hair loss is extremely rare and usually only occurs in very severe, long-standing, and untreated cases where the follicles have been repeatedly and significantly damaged. For the vast majority of people, treating the seborrheic dermatitis is the key to regaining hair density. It’s truly empowering to know that taking action can make such a difference in preventing long-term hair loss.
Consistency is Key
Maintaining a healthy scalp isn’t a one-time fix when you have seborrheic dermatitis. It requires ongoing attention. Even when your symptoms improve, you might need to continue using a medicated shampoo once or twice a week to prevent future flare-ups. Think of it like managing a chronic condition – you learn what works for you and integrate it into your routine.
Regular check-ups with your dermatologist, especially if you experience changes in your scalp or hair, can also be beneficial. They can help you adjust your treatment plan as needed and provide ongoing support.
Conclusion
So, can seborrheic dermatitis lead to hair loss? Yes, it can. But the crucial takeaway is that this type of hair loss is typically temporary and reversible. The chronic inflammation and excessive scratching associated with seborrheic dermatitis can indeed disrupt your hair growth cycle and damage follicles, leading to increased shedding and thinning.
However, you are not powerless. By understanding the condition and committing to an effective treatment plan – which often includes medicated shampoos, topical treatments, and thoughtful lifestyle adjustments – you can control your seborrheic dermatitis, reduce inflammation, prevent further hair loss, and encourage healthy regrowth. Don’t let the fear of hair loss paralyze you. Take action, consult a dermatologist, and be consistent with your care. A healthy scalp and fuller hair are well within reach.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does seborrheic dermatitis always cause hair loss?
No, seborrheic dermatitis does not always cause hair loss. While it can contribute to temporary hair thinning and shedding, particularly in more severe or prolonged cases, many individuals with the condition never experience noticeable hair loss.
Is hair loss from seborrheic dermatitis permanent?
Hair loss caused by seborrheic dermatitis is almost always temporary and reversible. Once the underlying scalp inflammation is effectively managed and the condition is brought under control, hair follicles can recover, and healthy hair growth typically resumes.
How quickly can hair regrow after treating seborrheic dermatitis?
Hair regrowth is a gradual process. Once seborrheic dermatitis is managed, it can take several weeks to a few months to notice new hair growth. Consistency with treatment and patience are key to seeing results.
What type of shampoo is best for seborrheic dermatitis and hair loss?
Medicated shampoos containing active ingredients like ketoconazole, zinc pyrithione, selenium sulfide, or salicylic acid are often recommended. Rotating between shampoos with different active ingredients can also be effective in managing seborrheic dermatitis and promoting scalp health.
Can scratching make seborrheic dermatitis hair loss worse?
Yes, excessive scratching can significantly worsen hair loss by physically dislodging hairs, damaging the hair shaft, and further irritating the already inflamed scalp. Minimizing scratching is crucial for hair preservation and overall scalp health.
When should I see a doctor for seborrheic dermatitis and hair loss?
You should see a dermatologist if over-the-counter treatments are ineffective, your symptoms are severe, you’re experiencing significant or persistent hair loss, or if the condition is causing you distress. A professional can provide an accurate diagnosis and a personalized treatment plan.
